As I do a lot of testing and CI in my day job, I took ELK for a test drive. (ELK stands for ElasticSearch, LogStash and Kibana)
I’ve played around with Logstash before, but it’s first time i’m trying Kibana.
I’ve look for a quick way to setup it, and there where gazillion hits in Docker Hub (I’ve forgot which one I’ve actually installed :)) EDIT: it was cyberabis/docker-elkauto.
That went quick quickly, with a small change that I’ve used port 81
Next thing I wanted to feed it with some data, good thing someone else added some key=value files to our CI just a few days ago (Thanks Mike). And I had first real data in to play with in matter of minutes
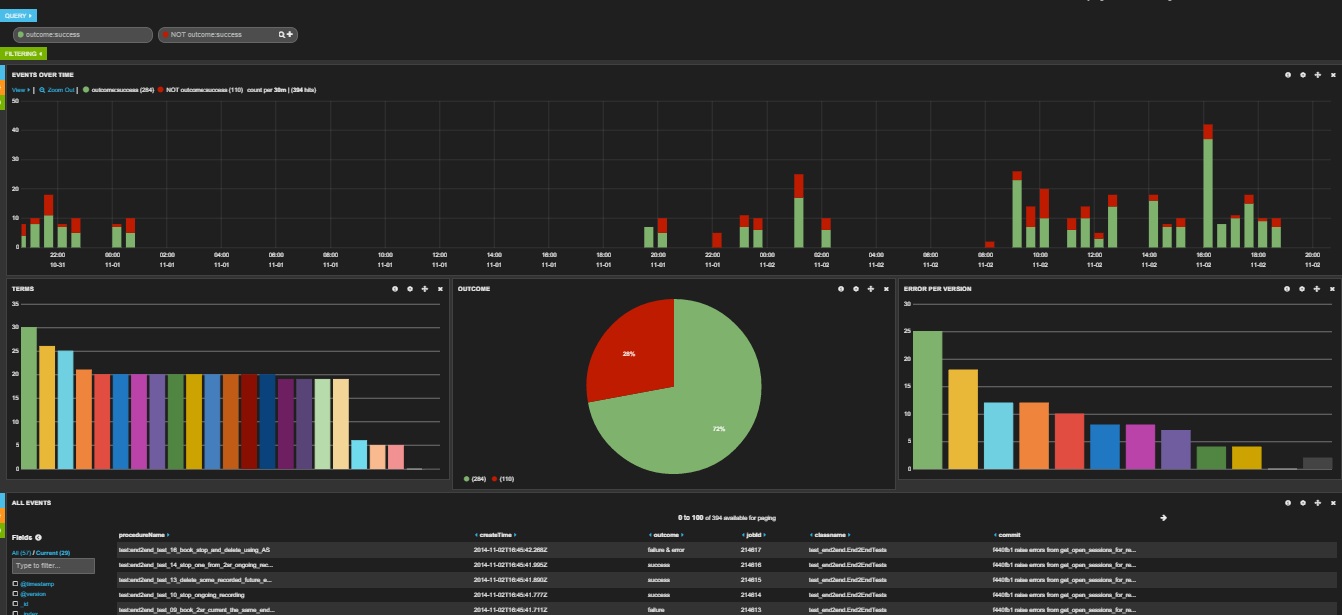
That’s was not enough for me, I wanted all the information from my tests. Seem like the junit-xml output has all the information I wanted. I hated the idea of running something after the tests are running, I wanted it to run automatic on any test I’ll run with py.test.
Took me some time to figure it out which py.test hook fits the best, and here’s how it can be done:
# content of conftest.py
def collect_ec_data():
"""
if we run in EC, collect all data we need
if not in EC, collect only commit and commit_sha
:return: dict
"""
# lets assume you don't really want to know what we save in our setup :)
return data_collected
def send_to_elk(item):
"""
send `item` to Logstash port
:param item: dict
:return: None
"""
s = socket.socket(socket.AF_INET, socket.SOCK_STREAM)
s.connect((TCP_IP, TCP_PORT))
logger.info("Sending to %s:%d", TCP_IP, TCP_PORT)
s.sendall(json.dumps(item) + '\n')
s.close()
def find_test_data(junit_xml_filename):
"""
flatten all the data from junit based xml file into a list of dicts
:param junit_xml_filename: the output from py.test --junit-xml
:return:
"""
tests_list = []
xml_test = open(junit_xml_filename, 'r').read()
et = ElementTree.fromstring(xml_test)
for test in et.iter('testcase'):
item = dict(**test.attrib)
outcome = None
failure = test.find("failure")
error = test.find("error")
skipped = test.find("skipped")
if failure is not None:
item['failure_message'] = failure.text
outcome = 'failure'
elif skipped is not None:
item['skip_message'] = skipped.attrib['message']
outcome = 'skipped'
elif error is not None:
item['error_message'] = error.text
outcome = 'error'
else:
outcome = 'success'
item['outcome'] = outcome
item['run_time'] = item['time']
# time is a built in in Logstash
del item['time']
tests_list.append(item)
# filter by group, and merge result
cumulative_keys = ['outcome', 'run_time']
tests_list_grouped = []
for key, group in groupby(tests_list, lambda x: (x['name'], x['classname'])):
item = dict()
for thing in group:
# merge needed values
if item.has_key('outcome'):
item['outcome'] += " & " + thing['outcome']
if item.has_key('run_time'):
item['run_time'] += thing['run_time']
# overwrite the rest
for key in thing.keys():
if key not in cumulative_keys or not item.has_key(key):
item[key] = thing[key]
tests_list_grouped.append(item)
return tests_list_grouped
def pytest_unconfigure():
junit_file = pytest.config.option.xmlpath
ec_data = collect_ec_data()
log_dir = os.environ.get('LOG_DEST_DIR', './')
if junit_file: # if found xml file, send all of it
tests_list = find_test_data(junit_file)
for i, test in enumerate(tests_list):
item = dict(**ec_data)
item.update(test)
# save data to a file
with open(os.path.join(log_dir, 'job_info%d.json' % i), 'w+') as f:
f.write(json.dumps(item, sort_keys=True,
indent=4, separators=(',', ': ')))
send_to_elk(item)Just for reference, to show how simple is the logstash configuration, almost untouched:
input {
tcp { port => 3333 type => "text event"}
tcp { port => 3334 type => "json event" codec => json_lines {} }
}
filter {
if [createTime] {
date {
match => [ "createTime", "ISO8601" ]
target => "@timestamp"
}
}
}
output { elasticsearch { host => localhost } }
ELK is a great combo, me like a lot…